The ability to choose the right cable cross-section can be useful to anyone over time, and you don’t have to be a qualified electrician to do this. By incorrectly calculating the cable, you can expose yourself and your property to serious risk - too thin wires will get very hot, which can lead to a fire.
Why do you need to calculate the cable cross-section?
First of all, carrying out this slightly complicated procedure is necessary to ensure the safety of both the premises itself and the people in it. Today, humanity has not invented a more convenient method of distribution and delivery electrical energy to the consumer, as if by wire. People need the services of an electrician almost every day - someone needs to connect an outlet, someone needs to install a lamp, etc. From this it turns out that even such a seemingly insignificant procedure as installing a new lamp is associated with the operation of selecting the required cross-section . What then can we say about connecting an electric stove or water heater?
Failure to comply with the standards can lead to damage to the integrity of the wiring, which often causes a short circuit or even electric shock.

If you make a mistake when choosing a cable cross-section and purchase a cable with a smaller conductor area, this will lead to constant heating of the cable, which will cause destruction of its insulation. Naturally, all this negatively affects the life of the wiring - there are often cases when, a month after successful installation, the electrical wiring stopped working and specialist intervention was required.
It should be remembered that the electrical and fire safety in the building, and therefore the lives of the residents themselves, directly depends on the correctly selected cable cross-section.
Of course, every owner wants to save as much as possible, but you should not do this at the cost of your life, putting it at risk - after all, as a result of a short circuit, a fire may occur, which may well destroy all property.
To avoid this, before starting electrical installation work, you should select a cable with an optimal cross-section. For selection, several factors must be taken into account:
- the total number of electrical devices located in the room;
- the total power of all devices and the load they consume. To the obtained value you should add 20–30% “in reserve”;
- then, through simple mathematical calculations, convert the resulting value into the cross-section of the wire, taking into account the material of the conductor.
Attention! Due to lower electrical conductivity, wires with aluminum conductors must be purchased with a larger cross-section than copper ones.
What affects the heating of wires
If during operation household appliances If the wiring heats up, you should immediately take all necessary measures to eliminate this problem. There are many factors influencing the heating of wires, but the main ones include the following:
- Insufficient cable cross-sectional area. To put it in accessible language, we can say this: the thicker the wires of the cable, the more current it can transmit without overheating. The value of this value is indicated in the marking of cable products. You can also measure the cross-section yourself using a caliper (you should make sure that the wire is not live) or by the type of wire.
- Material from which the wire is made. Copper conductors transmit voltage better to the consumer and have lower resistance compared to aluminum conductors. Naturally, they heat up less.
- Core type. The cable can be single-core (the core consists of one thick rod) or multi-core (the core consists of large number small wires). A multi-core cable is more flexible, but is significantly inferior to a single-core cable in terms of the permissible strength of the transmitted current.
- Cable laying method. Tightly laid wires located in the pipe heat up noticeably more than open wiring.
- Material and quality of insulation. Inexpensive wires, as a rule, have low quality insulation, which negatively affects their resistance to high temperatures.

How to calculate power consumption
You can calculate the approximate cable cross-section yourself - it is not necessary to seek the help of a qualified specialist. The data obtained as a result of the calculations can be used to purchase wires, however, the electrical installation work itself should be trusted only to an experienced person.
The sequence of actions when calculating the section is as follows:
- A detailed list of all electrical appliances in the room is compiled.
- The passport data of the power consumption of all found devices is established, after which the continuity of operation of a particular equipment is determined.
- Having identified the value of power consumption from devices that operate constantly, you should sum this value by adding to it a coefficient equal to the value of electrical appliances that turn on periodically (that is, if the device will work only 30% of the time, then you should add a third of its power).
- Next, we look for the obtained values in a special table for calculating the wire cross-section. For greater guarantee, it is recommended to add 10-15% to the obtained power consumption value.
To determine the necessary calculations for selecting the cross-section of electrical wiring cables according to their power within the network, it is important to use data on the amount of electrical energy consumed by devices and current appliances.
At this stage it is necessary to take into account important point– data from electrically consumed devices does not provide an exact, but an approximate, average value. Therefore, about 5% of the parameters specified by the equipment manufacturer must be added to this mark.
Most far from being the most competent and qualified electricians are confident in one simple truth - in order to correctly carry out electric wires for lighting sources (for example, for lamps), it is necessary to take wires with a cross-section equal to 0.5 mm², for chandeliers - 1.5 mm², and for sockets - 2.5 mm².
Only incompetent electricians think about this and think so. But what if, for example, a microwave, kettle, refrigerator and lighting operate simultaneously in the same room, which require wires with different cross-sections? This can lead to the most different situations: short circuit, rapid deterioration of wiring and insulating layer, as well as fire (this is a rare case, but still possible).
Exactly the same not very pleasant situation can happen if a person connects a multicooker, a coffee maker and, say, a washing machine to the same outlet.
Features of calculating the power of hidden wiring
If project documentation If the use of hidden wiring is implied, then it is necessary to purchase cable products “with a reserve” - about 20–30% should be added to the obtained value of the cable cross-section. This is done to avoid heating the cable during operation. The fact is that in conditions of cramped space and lack of air access, heating of the cable occurs much more intensely than when installing open wiring. If in closed channels it is planned to lay not one cable, but several at once, then the cross-section of each wire should be increased by at least 40%. It is also not recommended to pack tightly various wires- ideally, each cable should be contained in a corrugated pipe, which provides it with additional protection.
Important! It is by the value of power consumption that professional electricians are guided when choosing a cable cross-section, and only this method is correct.
How to calculate cable cross-sections by power
If the cable cross-section is sufficient electricity will pass to the consumer without causing heating. Why does heating occur? We will try to explain as clearly as possible. For example, a kettle with a power consumption of 2 kilowatts is plugged into the outlet, but the wire going to the outlet can only transmit a current of 1 kilowatt for it. The cable capacity is related to the resistance of the conductor - the greater it is, the less current can be transmitted through the wire. As a result of high resistance in the wiring, the cable heats up, gradually destroying the insulation.
With the appropriate cross-section, the electric current reaches the consumer in full, and the wire does not heat up. Therefore, when designing electrical wiring, you should take into account the power consumption of each electrical device. This value can be found from the technical data sheet for the electrical device or from the label affixed to it. By summing the maximum values and using a simple formula:
and get the value of the total current.
Pn denotes the power of the electrical appliance indicated in the passport, 220 is the rated voltage.
For a three-phase system (380 V), the formula looks like this:
I=(P1+P2+....+Pn)/√3/380.
The resulting I value is measured in Amperes, and based on it, the appropriate cable cross-section is selected.
It is known that the throughput copper cable is 10 A/mm, for aluminum cable the throughput value is 8 A/mm.
For example, let’s calculate the cable cross-section for connection washing machine, the power consumption of which is 2400 W.
I=2400 W/220 V=10.91 A, rounding up we get 11 A.
11 A+5 A=16 A.
If we take into account that three-core cables are used in apartments and look at the table, then the value close to 16 A is 19 A, so to install a washing machine you will need a wire with a cross-section of at least 2 mm².
Table of cable cross-sections relative to current values
| Current cross-section wire length of core(mm 2) | Current (A), for wires laid | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open That | in one pipe | |||||
| two one- vein | three one- vein | four one- vein | one two- vein | one three- vein |
||
| 0,5 | 11 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 0,75 | 15 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 15 | 14 |
| 1,2 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 15 | 16 | 14,5 |
| 1,5 | 23 | 19 | 17 | 16 | 18 | 15 |
| 2 | 26 | 24 | 22 | 20 | 23 | 19 |
| 2,5 | 30 | 27 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 21 |
| 3 | 34 | 32 | 28 | 26 | 28 | 24 |
| 4 | 41 | 38 | 35 | 30 | 32 | 27 |
| 5 | 46 | 42 | 39 | 34 | 37 | 31 |
| 6 | 50 | 46 | 42 | 40 | 40 | 34 |
| 8 | 62 | 54 | 51 | 46 | 48 | 43 |
| 10 | 80 | 70 | 60 | 50 | 55 | 50 |
| 16 | 100 | 85 | 80 | 75 | 80 | 70 |
| 25 | 140 | 115 | 100 | 90 | 100 | 85 |
| 35 | 170 | 135 | 125 | 115 | 125 | 100 |
| 50 | 215 | 185 | 170 | 150 | 160 | 135 |
| 70 | 270 | 225 | 210 | 185 | 195 | 175 |
| 95 | 330 | 275 | 255 | 225 | 245 | 215 |
| 120 | 385 | 315 | 290 | 260 | 295 | 250 |
| 150 | 440 | 360 | 330 | - | - | - |
| 185 | 510 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 240 | 605 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 300 | 695 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 400 | 830 | - | - | - | - | - |
How to choose conductor cross-sections
There are several more criteria that the cross-section of the wires used must meet:
- Length of cable. The longer the wire, the greater the current loss observed in it. This again occurs as a result of an increase in resistance, which increases as the length of the conductor increases. This is especially noticeable when using aluminum wiring. When using copper wires to organize electrical wiring in an apartment, the length, as a rule, is not taken into account - the standard margin of 20–30% (for hidden wiring) is more than enough to compensate for possible increases in resistance associated with the length of the wire.
- Type of wires used. There are 2 types of conductors used in household electricity supply - copper or aluminum based. Copper wires are of better quality and have less resistance, but aluminum wires are cheaper. In full compliance with the standards, aluminum wiring copes with its tasks no worse than copper, so you need to carefully weigh your choice before purchasing a wire.
- Electrical panel configuration. If all the wires supplying consumers are connected to one circuit breaker, then it will be the weak point in the system. A heavy load will lead to heating of the terminal blocks, and non-compliance with the rating will lead to its constant operation. It is recommended to divide the electrical wiring into several “beams” with the installation of a separate machine.

In order to determine the exact data for choosing the cross-section of electrical wiring cables, it is necessary to take into account any, even the most insignificant parameters, such as:
- Type and type of insulation of electrical wiring;
- Length of sections;
- Laying methods and options;
- Peculiarities temperature regime;
- Humidity level and percentage;
- The maximum possible value of superheat;
- The difference in the powers of all current receivers belonging to the same group. All these and many other indicators can significantly increase the efficiency and benefits of energy use on any scale. In addition, correct calculations will help avoid cases of overheating or rapid abrasion of the insulating layer.
In order to correctly determine the optimal cable cross-section for any human household needs, it is necessary in all general cases to use the standardized following rules:
- for all sockets that will be installed in the apartment, it is necessary to use wires with an appropriate cross-section of 3.5 mm²;
- for all spotlighting elements, it is necessary to use electrical wiring cables with a cross-section of 1.5 mm²;
- As for high-power devices, cables with a cross-section of 4-6 mm² should be used.
If some doubts arise during the installation or calculation process, it is better not to act blindly. The ideal option would be to refer to the appropriate table of calculations and standards.
Copper cable cross-section table
| Cross-section of conductors (mm) | Copper conductors of wires and cables | |||
| Voltage 220 V | Voltage 380 V | |||
| Current (A) | Power, kWt) | Current (A) | Power, kWt) | |
| 1,5 | 19 | 4,1 | 16 | 10,5 |
| 2,5 | 27 | 5,9 | 25 | 16,5 |
| 4 | 38 | 8,3 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 6 | 46 | 10,1 | 40 | 26,4 |
| 10 | 70 | 15,4 | 50 | 33 |
| 16 | 80 | 18,7 | 75 | 49,5 |
| 25 | 115 | 25,3 | 90 | 59,4 |
| 35 | 135 | 29,7 | 115 | 75,9 |
| 50 | 175 | 38,5 | 145 | 95,7 |
| 70 | 215 | 47,3 | 180 | 118,8 |
| 95 | 265 | 57,2 | 220 | 145,2 |
| 120 | 300 | 66 | 260 | 171,6 |
Aluminum Cable Section Table
If you decide to independently replace or repair the electrical wiring installed around the house, you first need to answer the question: what cross-section of wire will be needed to perform this work efficiently. A properly selected cable will not only serve you for many years, but will also protect you from a lot of problems, the main one of which may be overheating of the wiring and, as a result, a short circuit or fire.
The choice of conductor material and cross-section can be done in two ways. The first is “by eye”, which is used by most home electricians, and which comes down to an arbitrary choice of electrical wire without taking into account the expected load, current consumption and other factors. The second is scientific, which is based on mathematical calculations based on electrical engineering data. Each metal used as an electrical wire has its own specific characteristics, and in order to make high-quality calculations, you need to know them. So, in a copper wire with a cross-section of 1 millimeter, the current density varies within 6-10 amperes, and in aluminum – 4-6 amperes. As the cross-sectional area increases, the throughput also increases. It is highly not recommended to exceed these figures, since the wires are not designed for high current and may not withstand the load. So, to determine the cable cross-section by power, calculate the total total power of all electrical appliances that will be connected to the network along one line. The calculation must be carried out with a reserve; to do this, multiply the resulting amount by the so-called simultaneity coefficient - 1.2. Then it is necessary to calculate the current strength sufficient to operate the devices. To do this, divide the resulting total power by your network voltage (usually 220 volts). Having received the desired value, you can easily select the wire of the required cross-section according to the table below of electrical installation rules.

Despite the fact that you have calculated the wire cross-section mathematically, taking into account all the nuances and laws of electrophysics, do not forget to install on the line circuit breaker It is recommended to use a three-core wire, one of the wires of which will be used for grounding. Knowing this and the above information, you can easily choose a cable that can withstand the load of all electrical appliances used in your home.
Major home renovations necessarily include replacement of electrical wiring. There are two main reasons for this action.
The first is the age of this wiring itself. As a rule, major or any serious repairs are carried out 15-20 years after the apartment is handed over. During this time, even a properly made home electrical network ages and wears out. This means it potentially becomes a source of danger for the inhabitants of the home.
The second reason is the redevelopment and major renovation of individual premises with the addition of new electrical appliances. Tie-ins and other connections of new wiring with old are extremely undesirable. Due to a mismatch in the characteristics of the cable or materials in it.
So, the question of whether to change the electrical wiring is considered resolved; it remains to deal with its practical implementation. And you need to start with choosing a cable.
Cable for electrical wiring in an apartment - 300 brands and 5000 varieties
Which side should we start with? A person who is far from electrical installation will grab his head. And there is something to grab onto. Because there are not just a lot of cables and wires, they literally cannot be counted, like Don Pedro in Brazil. Even professional electricians sometimes get overwhelmed and confused by the abundance of manufacturers and products.
The choice of wire for electrical wiring in an apartment is not only a question of the cost of repairs. A much more important point is that the wiring must ensure the “delivery” of electricity to any corner of the apartment and be safe, that is, not “bite” with current. And also be fire resistant and reliable.
Attention! The key to reliable electrical wiring is finding the right electrician. A specially trained technician must do electrical work and select cables for wiring in an apartment! Who has permission to perform electrical installation work and practical experience.
We will briefly talk about cables and wires, their cross-section, markings, materials and types. Let us explain what is suitable for home wiring and what cannot be used. So that you are aware of what your electrician is doing and why.
Characteristics of wires and cables that you should pay attention to when choosing
Let us immediately clarify that we are talking about a household power cable or wire with a voltage of 220/380 V for transmitting electric current in a home network. We are not currently considering all other types such as heating, television, computer and others.
The general list of characteristics looks like this:
- core material;
- design;
- section;
- thickness of conductor insulation;
- shell thickness;
- marking;
- core color;
- package;
- certificate;
- product condition.
1. Material and design
According to the composition of the vein, cable products are divided into copper and aluminum. Copper products are more reliable, the resistance is lower, the current is higher, and the heating is less when compared with aluminum of the same cross-section. In addition, copper oxidizes less and is more ductile, which means the cable lasts longer without loss of properties and characteristics.
Attention! Wiring aluminum cables in an apartment is prohibited according to the requirements of the PUE (electrical installation rules).
By design single-core (single-wire) and multi-core (multi-wire) cables and wires are produced. Single-core varieties are more rigid and inflexible, especially with a large conductor cross-section.
Answering the question “which wire to use for wiring under plaster,” we can say that theoretically a single-core single-wire copper cable is also suitable. Plaster will create additional protection for such a conductor. But in fact, no one lays a single-wire home electrical network.
Multi-wire single-core cable is softer and more flexible. It tolerates bends and turns well and is suitable for both open wiring and hidden wiring under plaster. It is the three-core single-wire that is now used for laying in apartments.

Attention! Do not confuse cables in which each core consists of one conductor with wires where the core is made of several conductors. Multi-wire cable products are prohibited for permanent installation in an apartment due to the high fire hazard. Read more about them in the block“which wires should not be used for electrical wiring in an apartment”
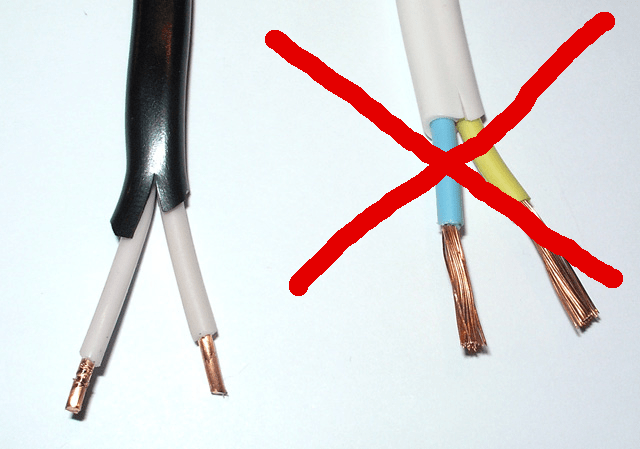
2. Cable cross-section for wiring in an apartment
It is measured in “squares”, that is, square millimeters and shows the throughput. For a copper cable, one “square” carries 8-10 Amperes of current, for an aluminum cable only 5 A. For safe operation, the conductor should be selected with a reserve of carrying capacity, which ensures heating of the wire within the permissible value, or, more simply, so that it does not “float” under the load. insulation. In addition, with hidden wiring, it must be taken into account that it is cooled less efficiently, which means that the cross-sectional reserve must compensate for this.
Attention! Do not confuse the cable cross-section with its diameter, these are two big differences! The diameter can be measured with a ruler, or better yet, with a caliper. And then substitute it into the formula and calculate the cross-sectional area.

Also remember that the choice of cable for wiring in an apartment is always rounded up. If the calculation results in 2.3 “squares”, a two and a half cable is selected, not two “squares”.
Ideally, the cross-section should match the marking on the cable tag, but in fact it often differs to a smaller extent. Small discrepancies are acceptable because the cable is certified by resistance, not by wire cross-section. If the discrepancies are significant, it is a marriage. An experienced electrician will see it visually, and you can measure the diameter of the core and calculate the cross-section for interest or to help a friend who independently decides to buy a cable for apartment wiring.
Some electricians advise using a cable with a rating higher than the calculated one. For example, 4 “squares”, instead of 2.5, to cover the “shortage” of the section, if there is one. But then you will have to calculate the wiring protection accordingly and install the correct machines and RCDs.
Advice! For electrical wiring in an apartment, we recommend a cross-section of copper wires from 1.5 to 2.5 square meters. mm. Allow two and a half “squares” for sockets and one and a half for lighting.
3. Wire insulation thickness
Each core in a multi-core or single-core cable has insulation made of PVC plastic of the usual type or with reduced flammability; polymers and cross-linked polyethylene are also used. The thickness of the insulation is regulated by GOST standards and it must be sufficient. For household cables ( Rated voltage up to 660V) with a cross section of 1.5 and 2.5 mm 2 the thickness of the insulating layer according to the standard is 0.6 mm. Deviations are allowed, but the insulation should not be thinner than 0.44 mm.
Simply put, there is a range of thicknesses where the insulation must “fit” so that the wiring serves reliably and there are no problems during installation. Whether the manufacturer violated the technology cannot be determined without a micrometer unless you tinker with the cables every day. Therefore, if there is no experienced electrician nearby, you should only buy cables from well-known brands in trusted stores.
4. Shell thickness
The sheath encloses the cable over the insulated cores, secures them and protects them. It is made, like the core insulation, from PVC plastic or polymer, but is thicker. For multi-core cables, the thickness is 1.8 mm, for single-core cables - 1.4 mm. Deviations in a smaller direction are also possible, but insignificant.
The insulating shell is a mandatory element. For any residential wiring cable, even with minimal power, double insulation is prescribed. That is, first on the core, and then on top of it. This ensures the safety of people and protects the conductor itself from damage.
5. Marking
This is the inscription on the cable sheath for installing electrical wiring in the apartment. It contains everything necessary information for selection. The inscription is printed or extruded during the manufacture of cable products. It should be clear, contrasting, and easily readable.
The labeling indicates:
- The brand of the product (cable or wire), which encodes the main properties and characteristics.
- Manufacturer's name.
- Year of issue.
- Number of cores
- Section.
- Voltage rating.
The inscription is applied along the entire length of the conductor at small intervals.
On the price tag and in catalogs of online stores, they usually do not indicate the year of manufacture and manufacturer and write the marking in the form VVGng(ozh)-0.66 kV 3x1.5 or VVG, VVGng cable 3x1.5.
It stands for three-core copper cable with a core cross-section of 1.5 “square” (3x1.5), single-wire core design (ozh). Insulation and sheath made of PVC compound (VV), flexible cable (G), non-flammable (ng). Rated voltage 660 Volts.
Remember! The letter designation of the cable brand begins with the core material; for aluminum the letter A is always used, for copper — the letter is not indicated, therefore all VVG brand cables of all modifications have copper wire Nick.
6. Core colors
What you need to know about the color is that it is either a solid color or a stripe is applied to the sheath along the entire cable, approximately a millimeter wide. This is the standard. Everything else, in the form of smears, spots, stripes across it, is from the evil one. And he says that strange people were making the cable in some basement.
There is a table for the colors of the cores that any experienced electrician knows. It describes what shade the main conductors are designated by - phase, neutral, grounding. This was done for convenience during installation, in order to see where to connect which conductor. Phase and working conductors may differ in color, but the “ground” is always “painted” yellow-green.

7. Packaging
Standard for all types is a coil or drum. The coils are sold to stores and wound onto drums for wholesalers, builders and other large buyers. In any case, a label with a description is attached to the cable.
The contents of the tag repeat the information on the inscription on the shell with some additions. It states:
- plant name or manufacturer's trademark
- product brand (designation)
- GOST or TU
- Date of issue
- number of segments with their length
- drum number
- conductor weight
- conformity mark
- OK mark.
If you come to buy a cable for wiring in an apartment in a whole bay of 100 m, you will receive a tag along with it. But if they cut off a piece for you, they won’t give you the label, you can just look at it.
8. Certificate
Needed to confirm that the cable is of high quality. Typically, products have 2 documents - a certificate of conformity, which is responsible for the suitability of the cable as an electrical installation material, and a certificate fire safety. You can ask the seller for them to review. Documents must be filled out indicating GOST standards for the cable and have a valid period, for example, until the end current year. As a rule, the documentation indicates specifications (technical conditions) in accordance with GOST and for cable products this is equivalent to compliance with GOST.
9. Condition
This is the appearance of the power wire. Pay attention to how the cable looks, because bruises, strong kinks, and compression hide an internal defect. The veins may be broken and even shorted to each other. It is clear that such material cannot be laid, therefore, do not be lazy to inspect the cable in the store, even before paying for your own purchase.
What cable is needed for wiring in an apartment?
We have already said that electrical wiring in an apartment “requires” 2 cable sections.
For sockets you need to take a cross section of 2.5 mm 2, because the switched load can reach 3-4 kilowatts. And a cable of two and a half “squares” is designed for a maximum power of up to 5.9 kilowatts and a current of up to 27 Amperes. This does not mean that you need to “load” the cable line to its limit. The choice always comes with a margin of one third of the planned load. Moreover, the cable lying under the plaster is cooled less efficiently and this is also taken into account when selecting.
For the lighting circuit, a cross section of 1.5 mm 2 is used. The load here is much less, but even if you decide to arrange illumination in the apartment, there will be plenty of current and power reserves.
Important information! Since modern electrical safety rules require grounding household electrical appliances and installing special sockets, a three-core cable is used for installation. In which there is a working phase conductor, a working zero and a protective zero.
Which cable does the online store site recommend for hidden wiring in a house or apartment?
Let us remind you that the marking contains the main characteristics of cable products. Letter designations indicate the materials of conductors, insulation, sheathing and flexibility, digital designations indicate the number of conductive conductors and their cross-section.
VVG cable
The most common domestic cable for electrical installation in an apartment. It has single-core copper conductors, insulation and a sheath made of PVC plastic, and is used in rooms with normal and high humidity. Designed for voltage up to 660 Volts. Refers to flexible, unarmored power cables. It can include from 1 to 5 cores, with a cross-section from one and a half to 240 “squares”. The conductor shape is round, flat or triangular.
VVG cables are available in several modifications:
- VVG - basic type with vinyl insulation and sheath;
- VVGng is a non-flammable power wire, the core insulation is self-extinguishing, that is, combustion does not spread;
- VVGng-LS - also has self-extinguishing non-flammable core insulation (ng) and a low smoke emission sheath;
- VVGng FR-LS - in addition to non-flammability and low smoke emission, this type of cable received additional fire protection from mica tape.
All brands with the ng prefix can be mounted in bundles, that is, several cable lines can be laid in one corrugation, pipe or pit.
| For sockets | For switches |
| VVGng 3x2.5 | VVGng 3x1.5 |
| VVGng-LS 3x2.5 | VVGng-LS 3x1.5 |
Conventional VVG is cheaper, but is not suitable for bundle laying and the shell is less fire-resistant and smoke-resistant. And the VVGng FR-LS brand is professional and is used in conditions of increased fire hazard in enterprises and is much more expensive.
NYM cable
European standard copper cable developed in Germany. Produced in Russian factories and complies with EU standards and GOSTs. The design is similar to the VVGng cable, rated voltage 660 V. Single-wire multi-core NYM cable with a cross-section of 1.5-10 mm2 and multi-wire with a cross-section of 16 mm2 are produced. The number of cores is 1-5, the insulation and sheath are made of PVC, non-flammability is provided by the rubber filler between the core insulation and the cable sheath.
Note! In stores you can find cheap cables marked NUM. This “typo” says that this is a copy with reduced characteristics. By purchasing it, you risk receiving low-quality products. We advise you to refrain from dubious savings on security.
VVGng and NYM cables have similar characteristics and advantages of use:
- High quality performance. The cores, insulation, and sheath comply with GOST and this makes the cable reliable.
- Convenient installation and easy cutting. The round cable is easy to install due to the absence of twists and is easier to seal when inserting.
- High fire resistance and safety. Compliance with standards ensures safe operation of the cable under load, and special insulation allows it to be laid in bundles, without the risk of fire from mutual heating.
- Self-extinguishing and low smoke. The shell material is self-extinguishing and slows down combustion. It also provides low smoke without dangerous halogens. If the protection works slowly, the damage from the fire will be minimal.
- Wide range of options in brands at a price to suit any budget.
Which wire is not suitable for wiring in an apartment?
And one more important point. We understand that for most people, “wire” and “cable” are synonymous. In fact, this is different types cable products. The main difference is that the cable always has a very strong two-layer insulation, with the first layer on top of the conductive cores and the second covering the entire bundle. Even if the cable has one core, the insulation is always double. The wire is a weaker structure with light insulation.
Note! Wiring your apartment with wire, even stranded or stranded, is a very bad idea.
The main problem with wires is their poor resistance to prolonged heating under constant load and their high flammability. Therefore, they do not comply with the requirements of the PUE for wiring in residential premises.
PVS wire
| PVS |
This is a copper connection wire with vinyl insulation and sheath. Used to connect household electrical appliances to the home network and to make extension cords. The number of conductors is 2-6, the core design is multi-wire, cross-section 0.75-10 mm2. Designed for a voltage rating of 380 V.
Attention! There is no need to take PVS wire for wiring on the advice of friends or to save money.
- Firstly, PVA have a multi-wire core structure. This means that all ends for connection must be tinned and soldered. This takes a lot of time and requires high-quality processing of the cores and extensive experience of the electrician.
- Secondly, the multi-wire construction of the core is a factor of increased fire hazard. Such a wire heats up more, which means the insulation wears out faster, which is dangerous and can result in a short circuit.
- Thirdly, the PVS wire cannot be laid in a bundle, like a cable. Only with the distance between the threads. That is, ditch the walls for each line separately.
So, the savings are very dubious and symbolic. The low price of the wire will be “eaten up” by the high cost of installation. And the quality of the wiring leaves much to be desired.
ShVVP and PVVP wire
| ShVVP, PVVP |
Installation cords or cables with single and multi-wire copper conductors. Used to connect electrical equipment and household appliances. They have a short service life; the stranded type requires processing of the ends and soldering during installation. They are not suitable for fixed wiring due to the lack of non-flammable insulation and poor characteristics.
Wire PUNP
Attention! PUNP has been banned for use for wiring since 2007 due to its unreliability.
Although there are “craftsmen” both among clients and among would-be electricians who use it. Motivating this by the fact that “all old apartments have this one.”
But “citizens” forget that since the times of the USSR, the equipment of household electrical equipment has changed greatly and its power has increased. That’s why PUNP was banned - it is low-power, has poor insulation and does not support modern loads.
The online store site offers only high-quality cables for electrical wiring in an apartment or house. Full list brands and types in the section:
Come in and choose your cable!
And also ask any questions. Funny and naive first of all! They are the most correct! Because it’s better to make electricians laugh than firefighters, wouldn’t you agree?
We always answer questions and talk about all the intricacies of installation. We quickly select a complete set for installing apartment wiring from cables to sockets and switches. We take into account your wishes and budget.
Call and ask! Phones
Find out the cable cross-section by power and wire length. We use effective online calculator wire diameter. Cables are fundamental elements in the process of transmitting and distributing current. They play an important role in connecting electricity, which is why it is necessary to accurately and accurately calculate the cable cross-section according to the length and load power in order to create favorable conditions for the uninterrupted flow of electricity and avoid negative emergency consequences.
If during design and development electrical network If the incorrect wiring diameter is selected, overheating and failure of various electrical equipment are possible. The cable insulation will also be damaged, which will lead to a short circuit and fire. There will be significant costs to restore not only the electrical wiring, but also all the electrical appliances in the room. To avoid this, you need to wisely select the cable cross-section in terms of power and length.
Online power cable selection calculator
Attention! If the data is entered incorrectly, the calculator may produce inaccurate values; for clarity, use the table of values below.
On our website you can easily make the necessary calculation of the wiring diameter in a few seconds, using a ready-made program to obtain data on the cross-section of the cable core.
To do this, you need to enter several individual parameters into the finished table:
- power of the proposed facility (total load indicators of all electrical appliances used);
- select the rated voltage (most often single-phase, 220 V, but sometimes three-phase - 380 V);
- indicate the number of phases;
- core material ( specifications wires, there are two compositions - copper and aluminum);
- line length and type.
Be sure to include all values. After that, click on the “calculate” button and get the finished result.
This value ensures that when calculating the cable cross-section by power online, the wire will not overheat under operating load. Ultimately, it is important to take into account the factor of voltage drop on the wire cores, while selecting parameters for a particular line.
Table for selecting wire cross-section depending on power (W)
How to independently calculate the cable cross-section along the length?
In domestic conditions, such data is necessary when manufacturing extension cords for long distance. However, even with accurately obtained results, you need to leave 10-15 cm in reserve for connecting wires (using welding, soldering or crimping).
In industry, the formula for calculating cable cross-section by power and length is used at the network design stage. It is important to accurately determine such data if the cable will have additional and significant loads.
Example of calculation in everyday life: I = P/U cosφ, where
I – current strength, (A);
P – power, (W);
U – network voltage, (V);
cosφ – coefficient equal to 1.
Using this calculation formula, you can find the correct wiring length, and cable cross-section indicators can be obtained using an online calculator, or manually. To convert Watts to Amps - .
Program for calculating cable cross-section by power
To find out the power of an equipment or device, you need to look at the tag, which indicates its main characteristics. After adding up the data, for example, 20,000 W, this is 20 kW. This indicator indicates how much energy all electrical appliances consume. If their percentage is used at a time about 80%, then the coefficient will be equal to 0.8. Calculation of cable cross-section by power: 20 x 0.8 = 16 kW. This is the core cross-section for a copper wire measuring 10 mm. For a three-phase circuit - 2.5 mm at a voltage of 380 V.
It is better to choose a wire of the largest cross-section in advance, in case of connecting unplanned equipment or devices. It’s better to add money today and do everything efficiently than to change the cable and buy a new kettle tomorrow.
A more detailed calculator that takes into account different coefficients.
Standard apartment wiring is designed for a maximum current consumption under continuous load of 25 amperes (copper wire with a cross-section of 5 mm and a diameter of 2.5 mm is used). The greater the planned current consumption, the more cores there should be in the cable. If the wire has a diameter of 2 mm, then its cross-section can be easily determined using the following formula: 2 mm × 2 mm × 0.785 = 3.14 mm 2. If you round the value, it turns out to be 3 mm squared.
To select a cable cross-section based on power, you need to independently determine the total current of all electrical appliances, add the result and divide by 220.
The choice for laying the cable depends on its shape; it is better to lay round wiring through walls, and for interior work, a flat cable is better suited, which is easy to install and does not create obstacles in operation. Their technical characteristics are the same.
Content:
Before connecting the load to the network, it is important to ensure that the supply cable cores are thick enough. If the permissible power is significantly exceeded, the insulation and even the core itself may be destroyed due to overheating.
Before calculating the cable cross-section by power, you should calculate the sum of the powers of the connected electrical appliances. In the majority modern apartments the main consumers are:
- Refrigerator 300 W
- Washing machine 2650 W
- Computer 550 W
- Lighting 500 W
- Electric kettle 1150 W
- Microwave oven 700 W
- TV 160 W
- Water heater 1950 W
- Vacuum cleaner 600 W
- Iron 1750 W
- Total 10310 W = 10.3 kW
In total, most modern apartments consume approximately 10 kW. Depending on the time of day, this parameter can decrease significantly. However, when choosing a conductor cross-section, it is important to focus on a larger value.
You need to know the following: the calculation of cable cross-section for single-phase and three-phase networks is different. But in both cases, three parameters should be taken into account first:
- Current strength(I),
- Voltage(U),
- Power consumption (P).
There are also several other variables, their meaning varies from case to case.
Calculation of wire cross-section for a single-phase network
Calculation of wire cross-section by power is carried out using the following formula:
I = (P × K u) / (U × cos(φ))
Where,
- I- current strength;
- P- power consumption of all electrical appliances in total;
- K and- simultaneity coefficient, usually the standard value of 0.75 is taken for calculations;
- U- phase voltage, it is 220 (V), but can range from 210 to 240 (V);
- Cos(φ)- for household single-phase appliances this value is unchanged and equals 1.
If you need to quickly calculate the current, you can omit the value of cos (φ) and even K and. The resulting value will differ downward (by 15%) if a formula of this type is used:
I=P/U
Having found the current using the calculation formula, you can safely proceed to selecting the power cable. More precisely, its cross-sectional area. There are special tables that present data that allows you to compare the current value, power consumption and cable cross-section.
The data varies greatly for conductors made from different metals. Today, for residential electrical wiring, only hard copper cable, aluminum is practically not used. Although in many old houses all lines are laid using aluminum.
The cross-section of the copper cable is selected according to the following parameters:

Calculation of wire cross-section in an apartment - Table
It often happens that the calculation results in a current that is between the two values presented in the table. In this case, the nearest larger value must be used. If, as a result of calculations, the current value in a single-core wire is 25 (A), it is necessary to select a cross-section of 2.5 mm 2 or more.
Calculation of cable cross-section for a three-phase network
To calculate the cross-section of the supply cable used in a three-phase network, you must use the following formula:
I = P / (√3 × U × cos(φ))
Where,
- I- current strength by which the cross-sectional area of the cable will be selected;
- U- phase voltage, 220 (V);
- Cosφ- phase shift angle;
- P- an indicator of the total power of all electrical appliances.
Cosφ is very important in this formula. Since it directly affects the current strength. It is different for different equipment; most often this parameter can be found in the technical accompanying documentation, or it is indicated on the case.
The total power of consumers is found very simply: all powers are added up, the resulting value is used for calculations.
A distinctive feature of the choice of cable cross-sectional area for use in a three-phase network is that a thinner core can withstand a larger load. The required section is selected according to the standard table.

Selection of cable cross-section for a three-phase network - Table
Calculation of the wire cross-section for power in a three-phase network is carried out using a value such as √3 . This value is necessary to simplify appearance formulas.
U linear = √3 × U phase
Thus, if necessary, you can replace the product of the root and phase voltage with linear voltage. This value is equal to 380 (V) (U linear = 380 V).
When choosing a cable cross-section, both for a three-phase network and for a single-phase network, it is necessary to take into account permissible continuous current . This parameter indicates the current strength (measured in amperes) that the conductor can withstand for an unlimited amount of time. It is determined using special tables, they are available in the PUE. For aluminum and copper conductors, the data differs significantly.

Permissible current duration - Table
When the value specified in the table is exceeded, the conductor begins to heat up. The heating temperature is inversely proportional to the current strength.
The temperature in a certain area can increase not only due to an incorrectly selected cross-section, but also due to poor contact.For example, in the place where wires are twisted. Quite often this happens as a result of direct contact between aluminum cables and copper cables. The surface of metals oxidizes and becomes covered with an oxide film, which significantly impairs contact. This is where the cable gets hot.
